Solar and Battery storage systems
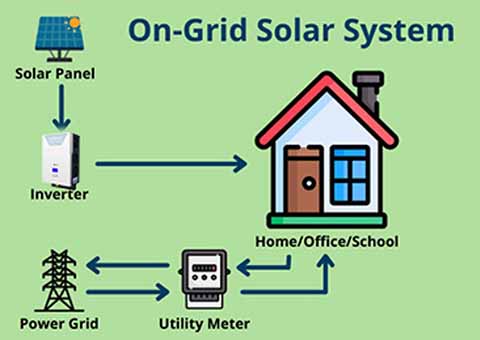
On Grid Solar System
- An on-grid solar system, also known as a grid-tied solar system, is a solar power setup
that is connected to the local utility grid. Here are some key features:1. Connection to the Grid: It relies on the existing electricity grid, allowing for the transfer of electricity between your solar system and the grid.
2. Net Metering: Homeowners can sell excess energy generated by their solar panels back to the grid, often through a system called net metering.
This can reduce electricity bills.3. No Battery Storage: On-grid systems typically do not include battery storage. They use grid power when solar production is low (e.g., at night or on cloudy days).
4. Cost-Effectiveness: Generally, on-grid systems are more affordable than off-grid systems due to lower installation and equipment costs.5. Dependence on Grid Availability: If there’s a power outage, the system usually shuts down for safety reasons, as it can't operate independently without batteries.
Solar On Grid System
Advantages
1.Good payback period without considering backup power source
Disadvantage
1. No backup power during power cuts
2. Need CEB clearance (If area transformer overloaded cannot be implement)
3. Need to invest additional amount for backup generator
4. Need more roof area
5. Shutdown power generation during day time power cuts
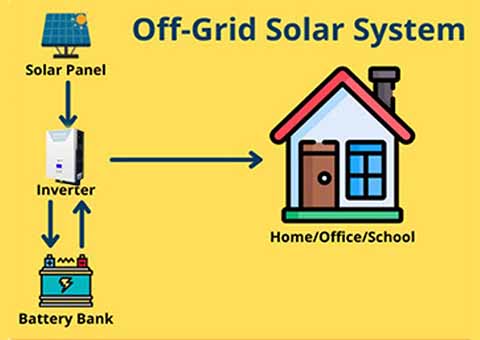
OFF Grid Solar System
- An off-grid solar system is a standalone solar power setup that operates independently of the utility grid. Here are the main features:
1. Self-Sufficient: Off-grid systems generate and store all the electricity needed for a home or facility without relying on the grid.2. Battery Storage: These systems include batteries to store excess solar energy generated during the day for use at night or during cloudy days.
3. Inverters: Off-grid systems require inverters to convert the direct current (DC) produced by solar panels into alternating current (AC) for household use.
4. Backup Generators: Some off-grid systems may incorporate backup generators to provide additional power during prolonged periods of low solar generation.
5. Remote Locations: Off-grid systems are often used in remote areas where grid access is unavailable or unreliable, making them a popular choice for cabins, rural homes, and emergency preparedness.
Advantages
- Good payback period
- No need to wait CEB clearance
- Have backup power during power cuts
- Need small roof area (3kW Solar panels)
- No need power generators for backup power
- Low investment
Note:- Customer has to change the tariff structure from GP1 to TOU.
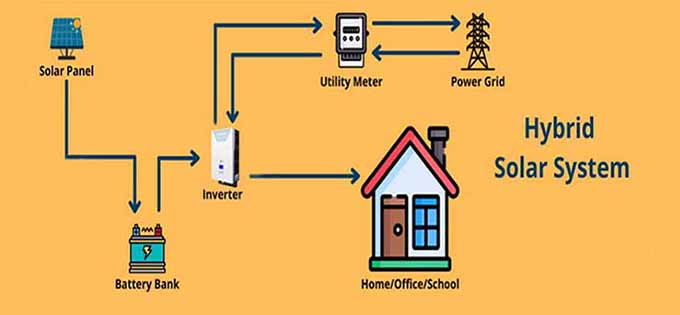
Hybrid Solar System
- A hybrid solar system combines features of both on-grid and off-grid solar systems. Here’s a breakdown of its key characteristics:
1. Grid Connection: Like on-grid systems, hybrid systems are connected to the utility grid, allowing users to draw power from the grid when needed.
2. Battery Storage: Hybrid systems include battery storage, enabling the storage of excess energy generated during the day for use at night or during outages.
3. Energy Management: These systems often come with advanced energy management systems that optimize the use of solar power, battery storage, and grid power, allowing for more efficient energy use.
4. Backup Power: In case of grid outages, a hybrid solar system can continue to supply power using the stored energy in batteries, providing reliable backup.
5. Flexibility: Users can choose to prioritize solar energy, grid energy, or battery storage based on their needs, making it a versatile option.
Hybrid Solar Systems
Advantages
Good payback period
Have backup power during power cuts
No need power generators for backup power.
Disadvantages
1. Need CEB approvals
2. Need large roof area for 7.5kW solar system
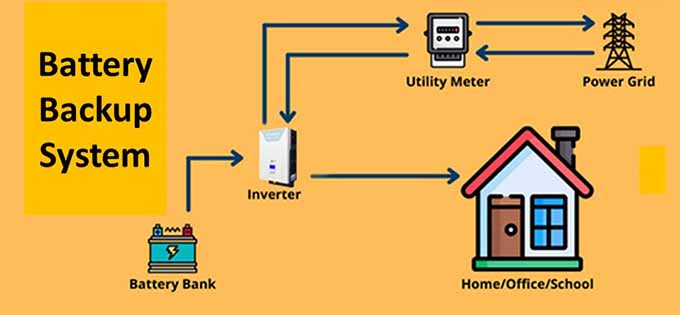
Battery Storage Systems
- Domestic load shifting using a battery storage system involves strategically managing the use of electricity to optimize energy consumption and reduce costs. Here’s how it works:
1. Storing Energy: During times of low electricity demand or when solar panels generate excess energy (typically during the day), the battery storage system charges by storing this surplus energy.
2. Using Stored Energy: During peak hours, when electricity rates are higher or when solar production is low (like at night), the stored energy is used to power household appliances and devices. This helps avoid using grid electricity at a higher cost.
3. Time-of-Use Tariffs: Many utility companies offer time-of-use pricing, where electricity rates vary throughout the day. Load shifting allows homeowners to take advantage of lower rates by using stored energy during peak pricing periods.
4. Load Management: Smart energy management systems can automate load shifting by determining the best times to charge and discharge the battery, ensuring that energy usage is optimized based on availability and costs.
5. Reducing Peak Demand: By using battery-stored energy during high-demand periods, homeowners can reduce their reliance on grid power, which can help decrease overall energy costs and reduce strain on the grid.
Battery Storage System
Advantages
Good payback period
Suitable for customers who are living in Apartments
No need to wait CEB clearance.
Have backup power during power cuts
No need a solar system
No need power generators for backup power
Low Investment
Note:- Customer has to change the tariff structure from GP1 to TOU.